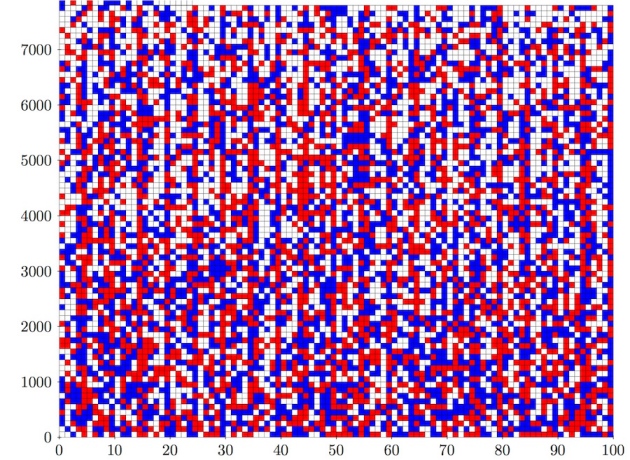
The numbers 1 to 7,824 can be coloured either red or blue so that no trio a, b and c that satisfies a2 +b2 = c2 is all the same colour. The grid of 7,824 squares here shows one such solution, with numbers coloured red or blue (a white square can be either). But for the numbers 1 to 7,825, there is no solution. NATURE.COM/Marijn Heule
PARIS—An Anglo-American trio presented the prize-winning solution to a 35-year-old math problem on Friday, but verifying it may be a problem in itself: reading it would take 10 billion years.
“Boolean Pythagorean Triples” is not a shameful contagious disease, but a long-unsolved enigma within a field called Ramsey Theory.
It was such a brain-teaser that nearly 30 years ago fabled American mathematician Roland Graham offered a cash prize to anyone who could solve it.
It was only $100, but still.
The self-declared winners—Marijn Heule, Oliver Kullmann and Victor Marek, of the universities of Texas, Swansea and Kentucky, respectively—unveiled their proof at the international SAT 2016 conference in Bordeaux, France.
By their own account, they cracked the puzzle “using Cube-and-Conquer, a hybrid satisfiability testing (SAT) method for hard problems.” As one would.
But colleagues, they acknowledged, needed to see the proof in the pudding, so to speak.
“Due to the general interest in this mathematical problem, our result requires a formal proof,” the numbers nutters explained in an abstract.
The resulting string of symbols is equivalent to “all the digitalized texts held by the US Library of Congress,” some 200 terabytes of data, according to the newsletter of France’s National Center for Research.
That’s 200,000 billion octets, for those more comfortable thinking in the base unit for digital information.
The problem itself is (almost) understandable.
It asks if it is possible to color positive whole numbers (such as 1, 2 or 3) either red or blue such that no sequence of numbers that satisfy Pythagoras’ famous equation—a2 + b2 = c2—are the same color.
If a and b are red, for example, then c could be blue. But all three could not be blue or red.
The proof shows that such a coloring scheme is, in fact, possible—up to the number 7,824. Beyond that, however, it doesn’t hold.
Crunching the numbers took two days of computer time on the Stampede supercomputer at the Texas Advanced Computing Center.
RELATED STORIES
Meet the man behind viral math puzzle
Keen to boost your brain? Play chess or read Plato