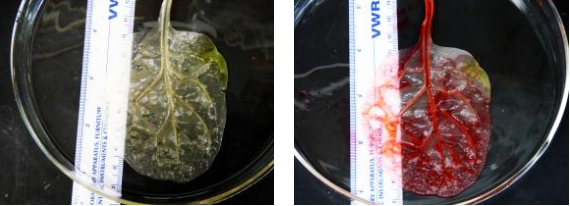
(Left) A decellularized spinach leaf before red dye is added to test its ability to filter blood much like a functioning human heart. Image from the Worcester Polytechnic Institute website.
The leafy-green vegetable spinach is perhaps best known as Popeye’s magical strength-boosting snack, but scientists have found a way to transform it into a beating heart.
In an effort to one day aid tissue regeneration in damaged organs, scientists from Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) in Massachusetts, USA, have developed a working human heart muscle using the edible plant.
The groundbreaking study, which was published in this month’s Biomaterial journals, is already being considered as the key to finally unlocking the secrets of tissue engineering.
According to National Geographic, scientists have already mimicked a working cardiovascular system using advanced methods like 3D printing. However, intricate details such as the small, delicate blood vessels, which are vital to tissue health, are still giving them fits.
“The main limiting factor for tissue engineering is the lack of a vascular network,” said study co-author and WPI graduate student Joshua Gershlak. “Without that vascular network, you get a lot of tissue death.”
Still, Gershlak and his team have broken ground with their innovation by using plant veins to replicate how human blood moves through tissue.
The brilliant scientists claimed that the match was perfect, since leaves contain several network of thin veins that deliver water and nutrients to their cells.
“Cellulose is biocompatible [and] has been used in a wide variety of regenerative medicine applications, such as cartilage tissue engineering, bone tissue engineering and wound healing,” the authors wrote in their paper.
As of this writing, the team is currently working on removing plant cells from the spinach leaf, in order to use its frame made of cellulose.
In the long term, the team is looking to apply its findings for heart attack patients or those with cardiac issues, in hopes of preventing their hearts from contracting.
The team is also looking to use other types of plants to repair other tissues in the human body. Khristian Ibarrola /ra