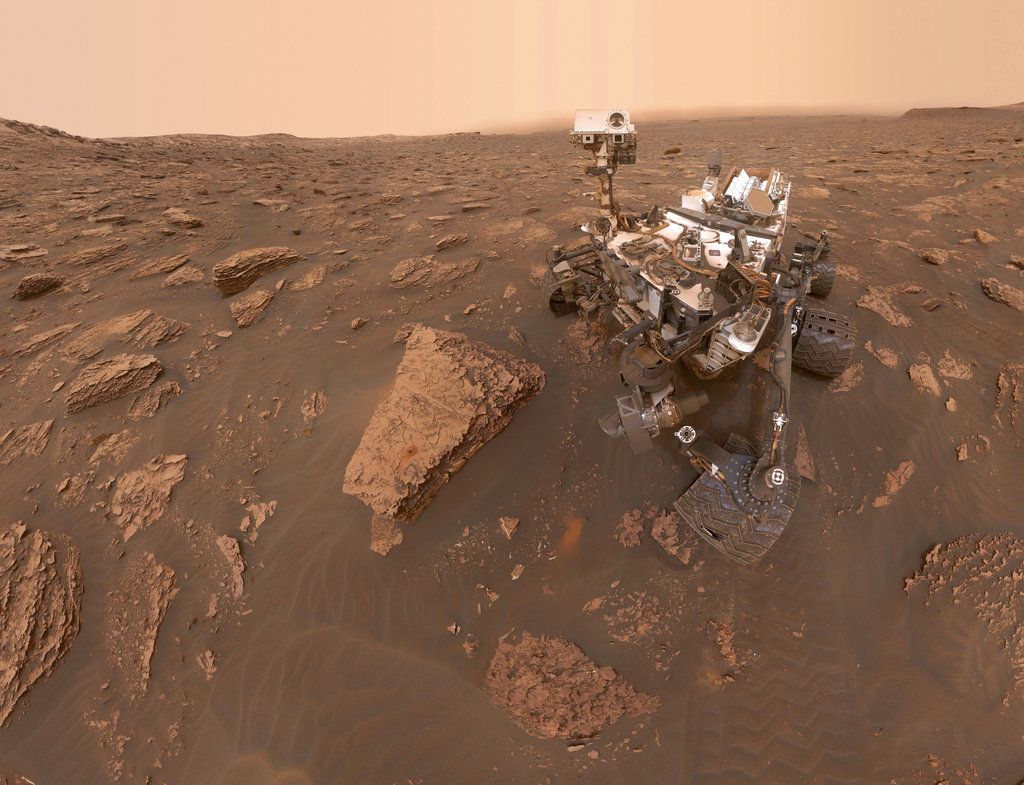
This composite image made from a series of June 15, 2018 photos shows a self-portrait of NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover in the Gale Crater. The rover’s arm which held the camera was positioned out of each of the dozens of shots which make up the mosaic. A dust storm has reduced sunlight and visibility at the rover’s location. (NASA/JPL-Caltech via AP)
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. — Mars has a nasty habit of living up to its mythological name and besting Earth when it comes to accepting visitors.
NASA’s InSight is the latest spacecraft to come calling, with every intent of landing and digging deeper into the planet than anything that’s come before. The lander arrives at Mars on Monday following a six-month journey.
“We’ve had a number of successful landings in a row now. But you never know what Mars will throw at you,” said Rob Grover, lead engineer for the landing team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Landing on Mars is always risky, Grover and other experts stress at every opportunity.
“Our job on the landing team is to be paranoid about what could go wrong and make sure that we’re doing everything we can to make sure things go right,” he said,
The numbers back him up. Only about 40 percent of all missions to Mars — named after the Roman god of war — have succeeded.
“Going to Mars is really, really hard,” NASA’s top science mission official, Thomas Zurbuchen, told reporters earlier this week. “As humanity, the explorers all over the world, we’re batting about 50 percent — or less.”
The United States is the only country to successfully operate a spacecraft on the Martian surface. InSight represents NASA’s ninth attempt to put a spacecraft on Mars; only one effort failed.
The last one — NASA’s Curiosity rover — is still on the move after six years, with more than 12 miles (20 kilometers) on its odometer. The space agency’s older, smaller Opportunity was roaming around up there until June, when a global dust storm knocked it out of service. Flight controllers haven’t given up hope yet that it will be revived.
Humanity’s nearly 60-year history of trying to get to Mars includes attempts to fly past the red planet for picture-taking without stopping, as well as the vastly more complicated efforts to put spacecraft into orbit around the red planet and to actually land.
NASA’s Mariner 4 performed the first successfully flyby of the red planet in 1965, sending back 21 photos.
Mariner 9 made it into orbit around Mars and beamed back more than 7,000 photos.
And NASA’s Vikings 1 and 2 not only put spacecraft into orbit around Mars in 1976, but on the surface, too. The twin Vikings were the first successful landers on Mars from planet Earth.
The 1990s weren’t as kind for NASA. A humiliating English-metric conversion screw-up doomed the Mars Observer in 1993. Another U.S. orbiter later was lost, as well as a lander and two accompanying probes meant to penetrate the surface.
Despite decades of trying, Russia, in particular, has had lousy luck at Mars.
The then Soviet Union was the first to attempt a flyby of Mars, in 1960. The spacecraft never reached Earth orbit. After more launch failures and flight mishaps, the Soviets finally got a pair of spacecraft into Mars orbit in 1971 and got back real data. But the companion landers were a total bust.
And so it’s gone for the Soviets/Russians through their most recent attempt with China in 2011.
The daunting goal was to land a spacecraft on Mars’ moon Phobos to collect and return samples, and to put a second spacecraft into orbit around Mars. Neither made it out of Earth orbit.
Europe also has been snake-bitten at Mars, as has Japan.
While the European Space Agency has satellites working around Mars, both of its landing attempts have flopped. Just two years ago, its lander hit the surface so fast, it dug out a crater. Japan’s sole Mars spacecraft, launched in 1998, didn’t make it into orbit.
India, meanwhile, has been operating a satellite around Mars for four years, its first and only shot at the red planet.
There’s a heavy European presence on NASA’s InSight. Germany is in charge of the mechanical mole that’s designed to burrow 16 feet (5 meters) into the Martian surface to take underground heat measurements, while France directs the lander’s quake-monitoring seismometer.
On the surface, Curiosity is the only thing operating on Mars. Currently in orbit: U.S. Odyssey since 2001, Europe’s Mars Express (2003), U.S. Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (2006), U.S. Maven (2014), India’s Mangalyaan orbiter (2014) and Europe’s Trace Gas Orbiter (2016). /muf