What we currently know about the global cyberattack
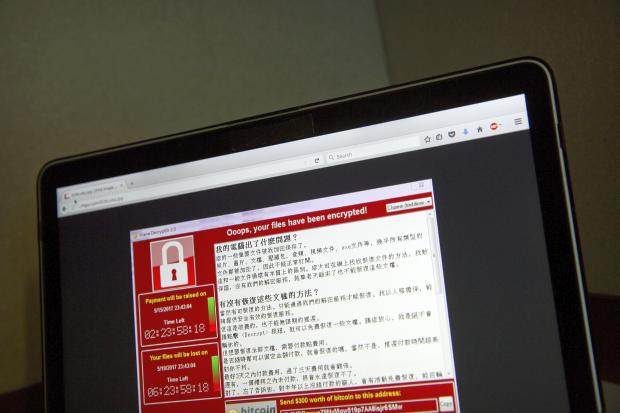
In this photo, taken May 13, 2017, a screenshot of the warning screen from a purported ransomware attack, as captured by a computer user in Taiwan, is seen on a laptop in Beijing. As danger from the global cyberattack continues to fade, analysts are starting to assess the damage. The good news: Hard-hit organizations such as the UK’s National Health Service appear to be bouncing back, and few people seem to have actually paid the ransom. The bad: This attack has demonstrated how a new automated form of malware can spread rapidly, potentially encouraging future hackers. (Photo by MARK SCHIEFELBEIN / AP)
NEW YORK — The danger from a global cyberattack that spread to some 150 nations continues to fade, and that’s only some of the good news.
After two security researchers greatly slowed down that attack , which effectively held people’s documents, photos and other digital files hostage, hard-hit organizations such as the UK’s National Health Service seem to be bouncing back. While it’s a crude measure of the impact, it also appears that relatively few of those affected were desperate enough to actually pay the ransom demanded by the attackers.
On the other hand, the attack has served as a live demonstration of a new type of global threat, one that could encourage future hackers.
Here’s what we currently know about the ransomware known as WannaCry, which locked up digital photos, documents and other files to hold them for ransom.
Where it came from
Researchers are still puzzling out how WannaCry got started. Figuring that out could yield important clues to the identity of its authors.
The malware spread rapidly inside computer networks by taking advantage of vulnerabilities in mostly older versions of Microsoft Windows. That weakness was purportedly identified and stockpiled for use by the US National Security Agency; it was subsequently stolen and published on the internet.
But it remains unclear how WannaCry got onto computers in the first place. Experts said its rapid global spread suggests it did not rely on phishing, in which fake emails tempt the unwary to click on infected documents or links. Analysts at the European Union cybersecurity agency said the hackers likely scanned the internet for systems that were vulnerable to infection and exploited those computers remotely.
Once established, WannaCry encrypted computer files and displayed a message demanding $300 to $600 worth of the digital currency bitcoin to release them. Failure to pay would leave the data scrambled and likely beyond repair unless users had unaffected backup copies.
Ransom payments
Investigators are closely watching three bitcoin accounts associated with WannaCry, where its victims were directed to send ransom payments. The digital currency is anonymized, but it’s possible to track funds as they move from place to place until they end up with an identifiable person.
So far, there have been no withdrawals from those accounts.
Given the scope of the attack, relatively few people appear to have actually paid the ransom. According to a Twitter account that monitors those accounts , they’ve received only about 250 payments worth a total of slightly more than $72,000.
North Korea
Several sets of investigators have now reported tentative findings that suggest hackers linked to North Korea might have been involved with WannaCry. But they could all be drawing conclusions from a very small set of clues.
On Monday, the Russian security firm Kaspersky Lab said portions of the WannaCry program use the same code as malware previously distributed by the Lazarus Group, a hacker collective behind the 2014 Sony hack. Another security company, Symantec, related the same findings, which it characterized as intriguing but “weak” associations, since the code could have been copied from the Lazarus malware.
Two law enforcement officials likewise said US investigators suspect North Korea based on code similarities; the officials called that finding preliminary. The officials spoke to The Associated Press on condition of anonymity because they aren’t authorized to speak publicly about an ongoing investigation.
But WannaCry remains a puzzle, in part because some of its elements seemed amateurish. Salim Neino, CEO of the Los Angeles-based security firm Kryptos Logic, said the WannaCry worm was “poorly designed” — patched together and consisting of a “sum of different parts” with an unsophisticated payment system.
Typical ransomware also generates a unique bitcoin account for each payment to make tracing difficult. That wasn’t done here.
Digging out
One of the organizations hardest hit by WannaCry — the UK’s National Health Service — appears to be recovering. On Friday, many NHS hospitals had to turn away patients after WannaCry locked up computers, forcing the closure of wards and emergency rooms.
NHS Digital, the body that oversees cybersecurity in Britain’s health system, said that as of now, it has “no evidence that patient data has been compromised.” The agency told hospitals to disconnect all infected computers, apply a Microsoft patch that closes the vulnerability, then “roll back” the infected computers and restore them from backed-up files.
UK hospitals are supposed to back up data frequently and at multiple locations. It’s possible that some data that wasn’t backed up could be lost.
Sign of hacks to come
WannaCry could also serve as a kind of template for future cyberattacks.
Neino of Kryptos Logic, for instance, said the leak of the NSA hacking tools have significantly narrowed the gap between nations and individuals or cyber gangs.
“The concern has always been, when are the real bad guys, the ones that don’t care about rules of engagement, the ones who are really out to hurt us, will they become cyber-capable?” he said in an interview Monday night with The Associated Press. “I think today we found out that those who really want to hurt us have begun to, because they became cyber-capable the moment that the NSA cybertools were released.”