Scientists: Saturn spent billions of years without its rings
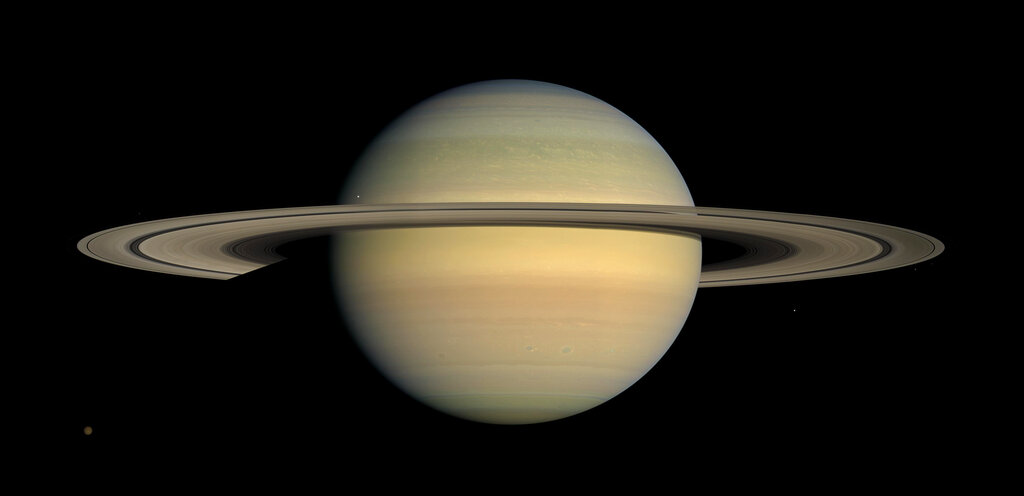
This July 23, 2008 image made available by NASA shows the planet Saturn, as seen from the Cassini spacecraft. On Thursday, Jan. 17, 2019, an Italian-led team reported in the journal Science that the planet’s primary rings appear to be 10 million to 100 million years old. Saturn, on the other hand, is 4.5 billion years old, like all our solar system’s planets. (NASA/JPL/Space Science Institute via AP)
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. — Saturn may have flown solo for billions of years — almost its entire existence — before getting its stunning set of rings, a new study suggests.
An Italian-led team reported Thursday in the journal Science that Saturn’s primary rings appear to be just 10 million to 100 million years old. The gas giant Saturn, on the other hand, is 4.5 billion years old, like all the other planets in our solar system.
The findings are based on data collected by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft while repeatedly diving between Saturn and its rings in 2017, shortly before its demise.
By estimating the mass of the rings through gravity measurements, the researchers gauged the age of the three main rings: A, B and C. It’s still a mystery, though, how these icy rings formed.
Scientists suspect a collision between two of Saturn’s many moons or perhaps a moon and comet.
The rings are made mostly of ice. The remaining 1 percent is dust and possibly organic contaminants. Overall, the material ranges in size from tiny particles, to pebbles, to boulders.
Lead researcher Luciano Iess, a planetary scientist at Sapienza University in Rome, said orbital motion sprayed the dust and other contaminants onto the icy rings at a constant rate. His team calculated the length of time it would take for the contaminants to accumulate — it turned out to be a “short” 10 million to 100 million years.
It’s possible the rings originally were denser than they are now and have thinned over time, which would put them more in line with Saturn’s age. But Iess said there’s little consensus for that theory.
Iess said NASA’s Voyager spacecraft — as well as Cassini — had already provided clues that the rings had not formed with Saturn. “But now we have much more concrete evidence, which was only possible to obtain during the final phase of the mission, called the Grand Finale,” he wrote in an email.
The only spacecraft to ever orbit Saturn, Cassini burned up as it plunged through the planet’s atmosphere.
The masses of Saturn’s fainter D, F, G and E rings are considered negligible, the researchers wrote.
Saturn’s E ring, meanwhile, has its own unique source: plumes of water vapor streaming into space from the moon Enceladus, believed to harbor an ocean beneath its surface.
Iess noted the latest findings are “another gift we received from this beautiful mission.”
“Cassini, like all giants, has left a legacy that will last for a long time,” he said.
Cassini was launched from Florida in 1997. It carried the European probe named Huygens, which separated and landed on Saturn’s moon Titan in 2005. /muf