7 billion years: Scientists say oldest solid material found
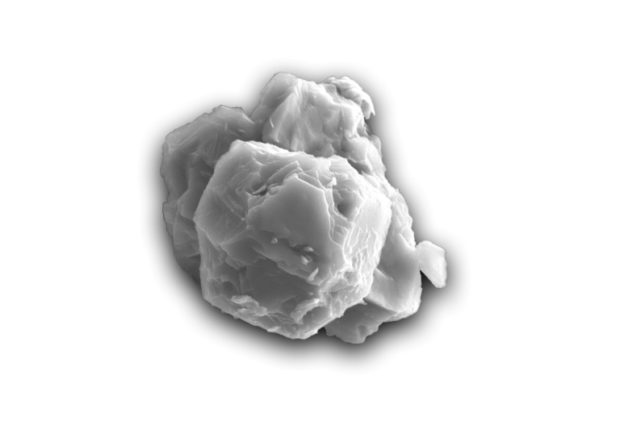
An undated handout picture shows a scanning electron micrograph of a presolar silicon carbide grain. Image: AFP/Janaína N. Ávila
Researchers said Monday that new techniques have allowed them to identify the oldest solid material ever found on earth.
The stardust, formed five to seven billion years ago, came from a meteorite that fell to Earth 50 years ago in Australia, they said in a paper published in the journal PNAS.
It came down in 1969 in Murchison, Victoria state, and scientists from Chicago’s Field Museum have possessed a piece of it for five decades.
Philipp Heck, curator of meteorites at the museum, examined pre-solar grains, which are bits of stardust that become trapped in meteorites, making them time capsules of the period before the sun was born.
“They’re solid samples of stars, real stardust,” Heck said in a statement.
When the first stars died after two billion years of life they left behind the stardust, which formed into the block which fell to earth as the meteorite in Australia.
Although researchers first identified the grains in 1987 their age could not be determined.
But Heck and other colleagues recently used a new method to date these grains, which are microscopic in size. They are from silicon carbide, the first mineral formed when a star cools.
To separate the ancient grains from the relatively younger ones, scientists crushed fragments of the meteorite into a powder. Then they dissolved it in acid, which left only the pre-solar particles.
“It’s like burning down the haystack to find the needle,” says Heck.
When dust is in space it is exposed to cosmic rays which slowly change its composition. This allows researchers to date it.
A decade ago, only 20 grains from the meteorite were dated by a different method. Now, researchers have been able to determine the age of 40 grains, most of which are between 4.6 billion and 4.9 billion years old.
These ages correspond to the moment when the first stars began to break up, and since that type of star lived for two to 2.5 billion years, the stardust can be as old as seven billion years.
“These are the oldest solid materials ever found, and they tell us about how stars formed in our galaxy,” Heck said.
The new dating by this team confirms an astronomical theory which predicted a baby boom of stars before the formation of our sun, instead of a constant rhythm of star formation.
“We basically came to the conclusion that there must have been a time in our galaxy when more stars formed than normal, and at the end of their lives they become dust-producing,” Heck told AFP.
The task now is to apply the same method on other meteorites.
But according to Heck, there are fewer than five known to be in collections and big enough to give up such secrets. IB/NVG
RELATED STORIES:
289 days and counting: NASA astronaut sets record for longest single spaceflight by a woman