Astronomers find solar system older than ours
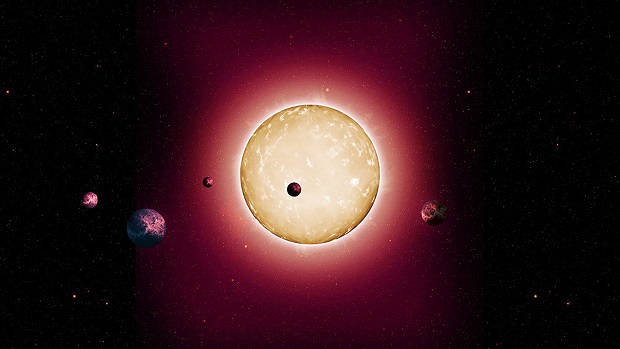
This artist’s rendering made available by Tiago Campante and Peter Devine shows the Kepler-444 star system, surrounded by at least five earth-sized planets. On Tuesday, Jan. 27, 2015, an international team of astronomers announced that this extrasolar system is 11.2 billion years old. With the age of the universe pegged at 13.8 billion years, this is the oldest star with close-to-Earth-size planets ever found. AP
CAPE CANAVERAL, Florida, United States — A newly discovered solar system — with five small rocky planets — makes ours look like a baby.
An international team of astronomers announced Tuesday that this extrasolar system is 11.2 billion years old. With the age of the universe pegged at 13.8 billion years, this is the oldest star with close-to-Earth-size planets ever found.
By comparison, our solar system is 4.5 billion years old.
The five planets are smaller than Earth, with the largest about the size of Venus and the smallest just bigger than Mercury. These planets orbit their star in less than 10 days at less than one-tenth the Earth’s distance from the sun, which makes them too close for habitation, said the University of Sydney’s Daniel Huber, part of the team.
“We’ve never seen anything like this — it is such an old star and the large number of small planets make it very special,” Huber said in a statement. “It is extraordinary that such an ancient system of terrestrial-sized planets formed when the universe was just starting out, at a fifth its current age.”
Lead researcher Tiago Campante of the University of Birmingham in England noted in a statement that by now knowing close-to-Earth-size planets formed so long ago, that “could provide scope for the existence of ancient life in the galaxy.”
Campante, an asteroseismologist, measured oscillations from the star to determine the age and size of this compact system.
NASA’s Kepler planet-hunting spacecraft was used to make the observations over a four-year period. Thus, the bright sunlike star at the heart of this system is named Kepler-444. It’s in the Constellation Lyre.
The team represented scientists from Europe, Australia and the United States. Their findings were reported in the latest edition of the Astrophysical Journal.
Kepler has discovered more than 1,000 confirmed exoplanets — planets outside our solar system — and nearly 4,200 candidates since its launch in 2009 and its revitalization in last year following a breakdown in its pointing system. It reached the 1,000-mark earlier this month.
RELATED SYSTEM
NASA finds more Earth-like planets outside solar system