WATCH: Google builds AI-powered AR microscope for faster cancer detection
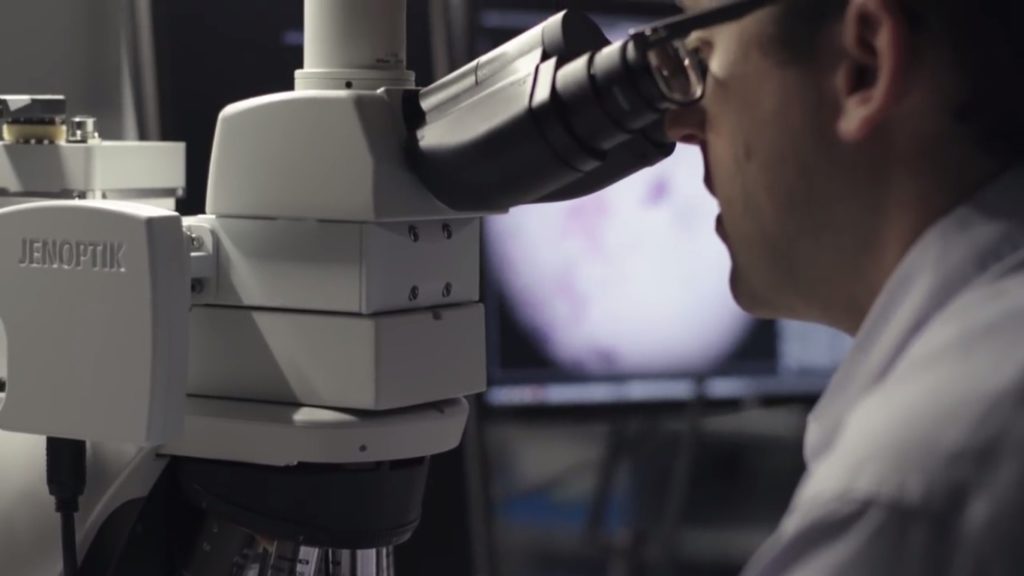

Image: YouTube/Google
Google integrated augmented reality (AR) technology and artificial intelligence (AI) with machine learning into a microscope to help doctors detect cancer faster.
Researchers made use of an AI trained through machine learning to help doctors pinpoint cancer cells whenever they look through a microscope. The paper documenting this study was presented during the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, in Chicago, Illinois, USA, being held from April 14 to 18.
The paper, titled “An Augmented Reality Microscope for Real-time Automated Detection of Cancer,” describes the use of an Augmented Reality Microscope (ARM) platform to detect cancer in cell sample slides with real-time assistance from an AI.
Using machine learning, the AI was trained to spot cancer cells through a team of pathologists going through thousands of slides. Once a slide is placed under the scope, the AI analyzes the cells in the slide through cameras. It then maps out the cancer cells by drawing a line around the affected area. This highlighting line can be seen by a pathologist through an AR Display when looking through the microscope. It’s like wearing AR glasses while looking through a microscope except that the glasses have been integrated.
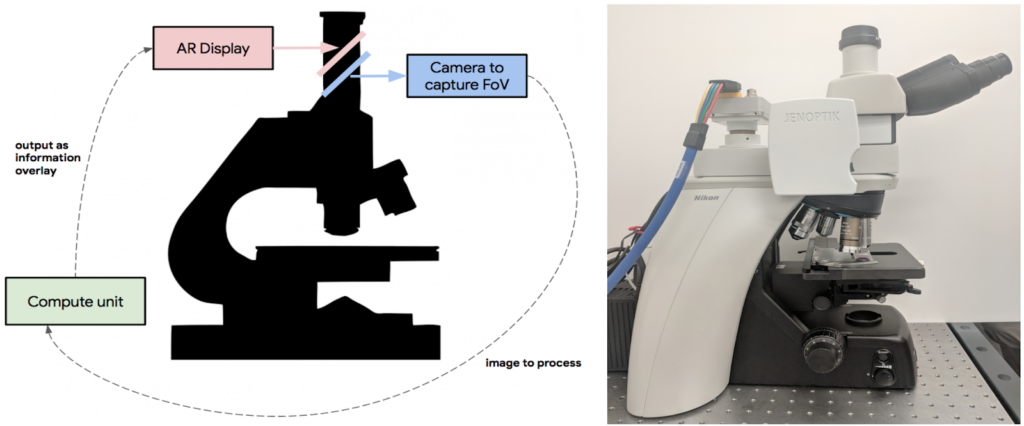
Image: Google
For now the ARM is able to accurately detect breast and prostate cancer cells.
The slides below show how the AI “encircles” what it thinks to be cancer cells. This is also what a pathologist would see when looking through the microscope.
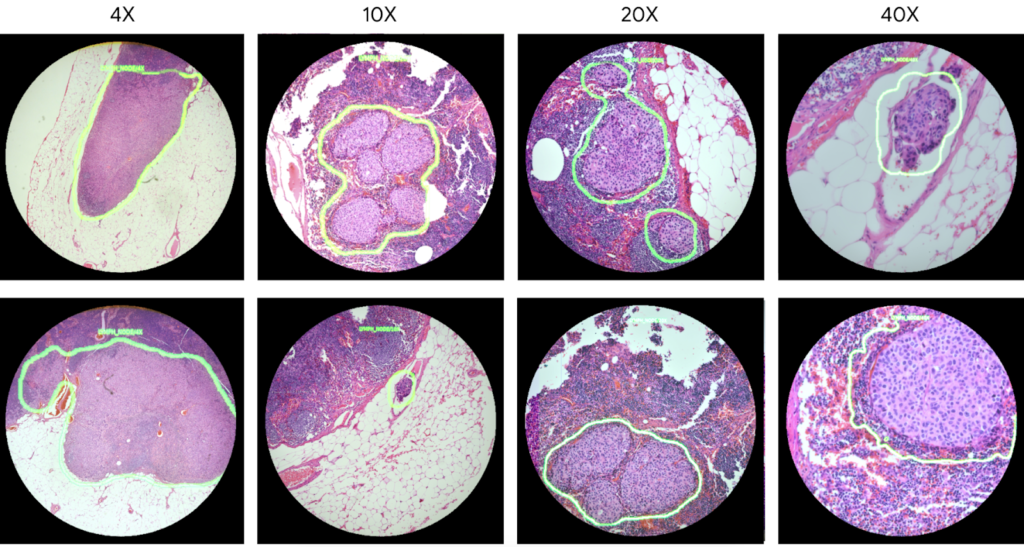
Image: Google
Apart from drawing lines around the affected area, the AI can also display text, arrows and heatmaps to help a pathologist determine cancer-affected areas.
The ARM AI can also be trained to help diagnose other diseases such as tuberculosis and malaria. Google sees the ARM being adopted in future digital pathology workflows in hospitals to speed up disease diagnosis, which could end up saving more lives.
The researchers also believe ARM can be applied to other industries that require the use of a microscope. Life science research and material science could benefit from the AI-assisted capabilities of ARM. /ra
RELATED STORIES:
Lying eyes: Google engineer developing tool to spot fake video
Web browsers to do away with users’ passwords
Apple warns employees to stop leaking information on future products